Table of Contents
ToggleContent Database and Glossary
.As your site grows, you have hundreds if not thousands of published blog posts, images, infographics, case studies, research papers, podcasts, it gets harder and harder for your site visitors to find whet they are looking for. So, in this lesson, I will show you two content hub models that will help your site visitors find what they are looking for.
If you are starting a new website, this may not be relevant to you but, it’s going to be a video for you to refer back to when your site has a huge database for blog posts.
The Content Database Model
The first model we are going to talk about is The Content Database Model. You know when you visit some fashion e-commerce sites, such as Lululemon, they allow you to filter their shop category such as “Men’s Running Clothes”. You can filter the size, the colour, the fabric, and many different attributes to display the product you are looking for.

Just like Ikea as well, you can filter the products of a given category. It will display all the products that match the filters you have applied.

Apply that to your database for blog posts. You have a ton of published articles, case studies, research papers, customer testimonials, infographics and many others. You just have to find similar attributes for all of your content and group them.
Content Database

I’ll show you some examples.
First is the content database of Lemlis. Now this is not a database for blog posts, they are email templates, many of them. So they have made it into a Contents Database.

You can filter the Emails by category, features and campaign type.
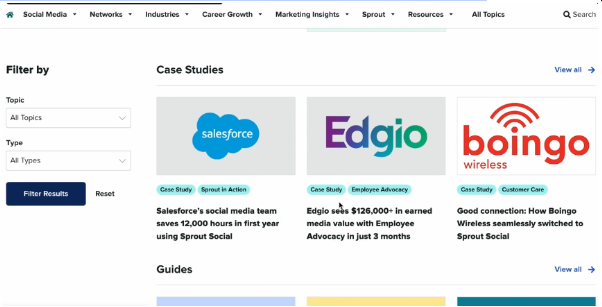
Another example would be again from Sprout Social. A site can have many different types of content hub. If we go to their “Resources” tab and “Resource Center” you’ll be led to their resource database.. You can filter the content of the site by Category and Topic.
So just like the focal function of an eCommerce Shop Category Page, the Content Database Model works the same.
As your site grows with many digital assets, it is logical to transition your blog into a Content Database. You don’t have to change the structure of your site but maybe build the database on top of the Gateway or Content Library Model.
Effective content creation involves generating engaging and relevant materials tailored to the needs and interests of a target audience.
The Glossary Model
Now, let me introduce you to another content model called The Glossary Model.
This is super-helpful for sites that have thousands of pages.
One of the most interesting Glossary Pages we’ve found is from Canva. This page teaches people about the meaning of colours. You can search for a colour if you know the name of it. For example: “purple” and it will have an Ajaz search function. This will bring you to the page that talks about the colour.
Back at the Glossary Page, as you scroll and hover to any of the colours, you will see the name of the colour.
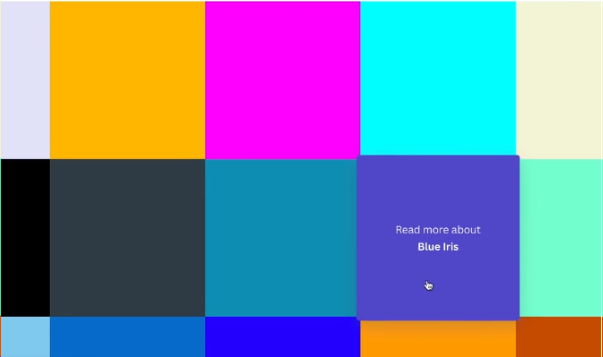
It is quite a neat way to present a glossary of different colours.
It is easy for people to find the colour they are looking for, And in terms of SEO, because this page is interesting, anybody who draws something that needs referenced would definitely want to link to this page. Because it acts like a tool, you can search for a colour and go through this beautiful Canva glossary page. Anf this page, internally, links to hundreds of different pages.
To demonstrate the SEO benefits, go to Google and search for “What is Amber Color” and you will see Canva’s page explaining the knowledge about the Amber colour.
This Glossary page only works if your content is visual and distinct. However, if a visual glossary page is not possible then check out these other examples.
The first example I want to show you is from Harvard Health Publishing.
This is their Medical Glossary Page which lists all the medical terms by letter. However, it would be more helpful to a glossary page, if each of these terms linked to an article that talked about the term.The first example I want to show you is from Harvard Health Publishing.

A better example would be from the Royal College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists, it has an accordian where you can expand the terms that start with a letter. The expanded description may have links toa page that explains the term.
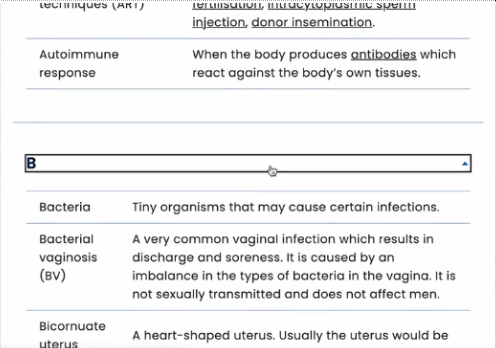
Another example that is not from a medical site, check out one.com’s glossary page. It lists every term and jargon there is related to web hosting. They have a neat alphabet menu at the top so that it is easy for site visitors to navigate the long list of terms and jargon.

So, basically, the glossary page will list all the terms and jargon in the niche or industry, and this model is more common than you think. There will be glossary pages for every niche or industry.
I’ve shared with you, 6 different ways to plan structure and organise your site. There is no perfect model, a website will always have a mix of different models.
Conclusion
A content database is a structured repository for managing and storing various types of digital content, such as articles, videos, images, and metadata. The content database model is a framework that defines how this content is organized, retrieved, and related to other data.
For example, a database for blog posts may include fields for titles, authors, tags, publication dates, and URLs, making it easy to index and retrieve posts. In practice, such a database supports seamless site structures, ensuring a consistent user experience and efficient content management.
Tools like Sprout Social often integrate with content databases to manage and distribute content effectively, leveraging the structured database content for scheduling, analytics, and audience engagement.